Privacy Risk Calculator v0.1
About this tool
Simplified Model
This privacy risk calculator considers the privacy risks imposed on a single group of individuals from a single group of threat actors. In a robust analysis, one should consider the risks imposed by multiple threat actors on all the affected individuals.
Risk Model
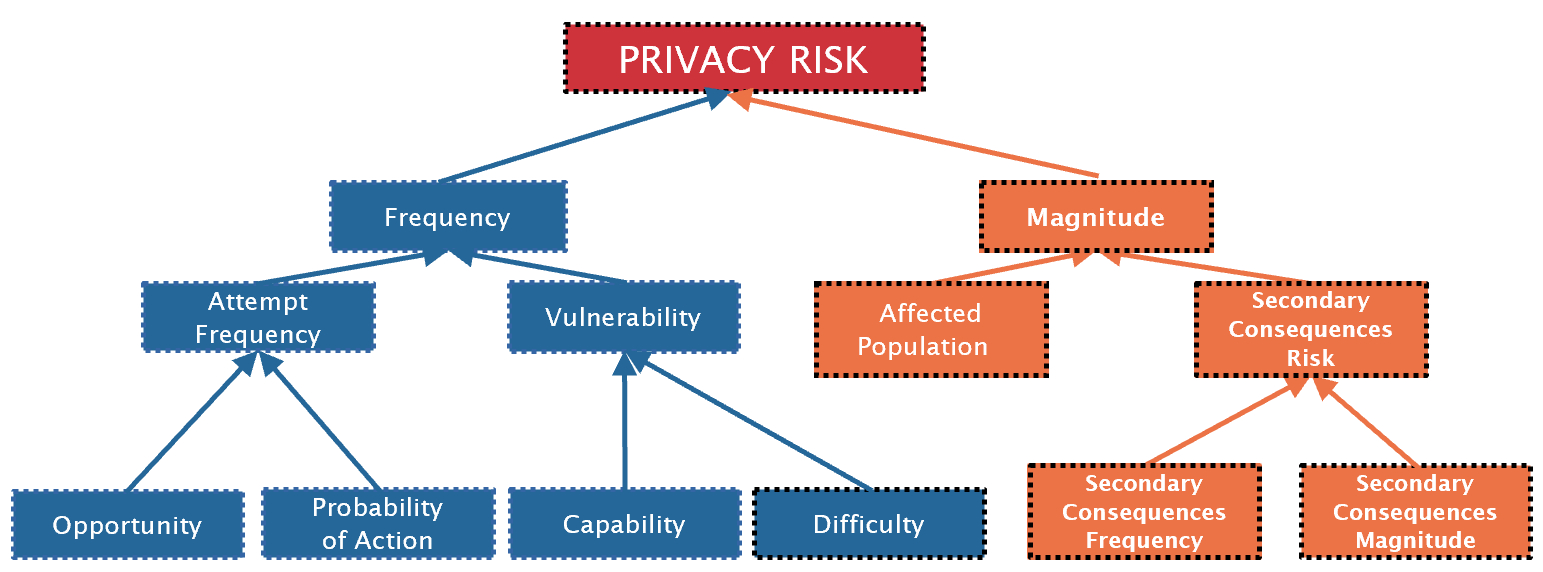
This risk model is based on a modified version of FAIR (Factors Analysis in Information Risk) [See below]. The calculator analyses risks to individuals, not organizational risk. The risk level is determined by the frequency that a privacy violation is committed against an individual and the magnitude of that violation across the population of affected individuals.
Magnitude
This tool uses the
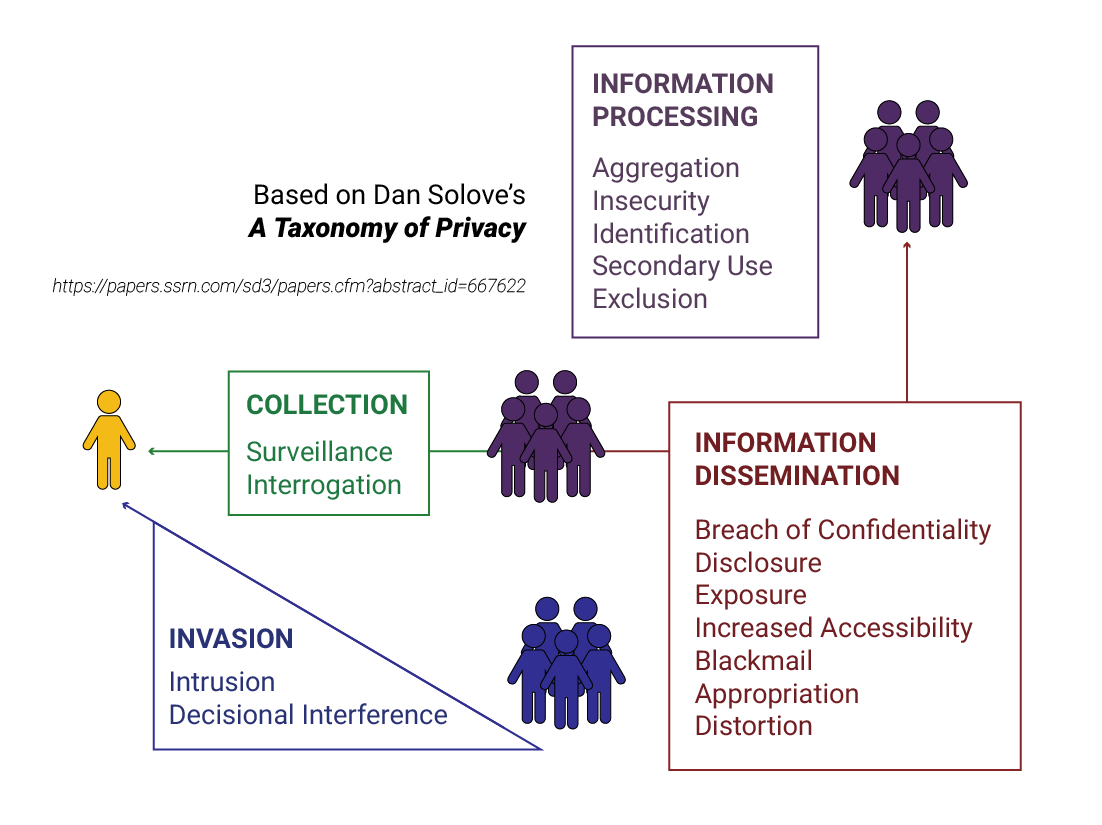
Solove Taxonomy of Privacy to identify the magnitude of consequences of certain activities. The goal of this is to identify and reduce the incidence of activities which social norms dictate are invasive of individuals privacy. For more information on why harms are considered secondary consequences under this model, see this article.
 .
.
Calculator Roadmap
- multiple threat actors
- saving results
- secondary consequences
- organizational consequences
- vulnerable populations
- risk tolerance
Describe the System
Primary Consequences
How to use this risk calculator
Each graph below will show three probability curves: a randomized population distribution, a risk profile for this threat actor committing this threat and your acceptable risk tolerance, as described above.| Your profile most likely looks like the graph at right. If your risk profile (in red) extends to the right of the population (in blue), this means that most individuals will expect more than one privacy violation per year. This means, you'll need to institute controls to mitigate these risks, after which your residual risk should be within your acceptable risk tolerance levels. [This tool currently does not provide a mechanism for assessing the effects of controls on your risk level] | 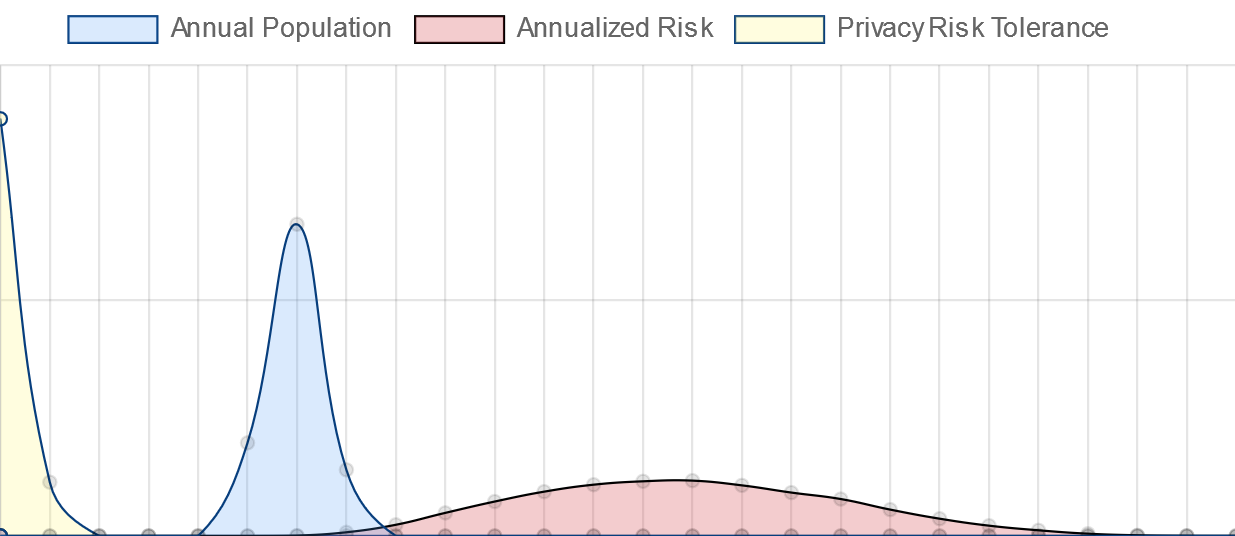 |
| If your risk profile is between the population and your risk tolerance (in yellow), then you have unacceptable privacy risks according to your risk tolerance level. | 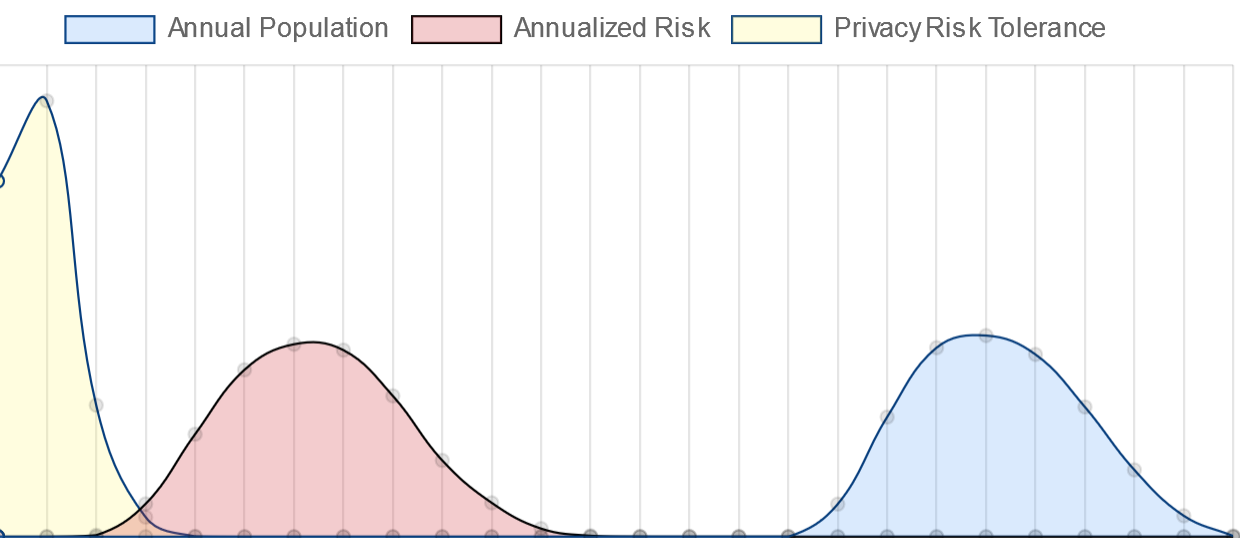 |
| If your risk profile falls to the left of or within the risk tolerance profile, congratulations, your privacy risks are within acceptable limits. | 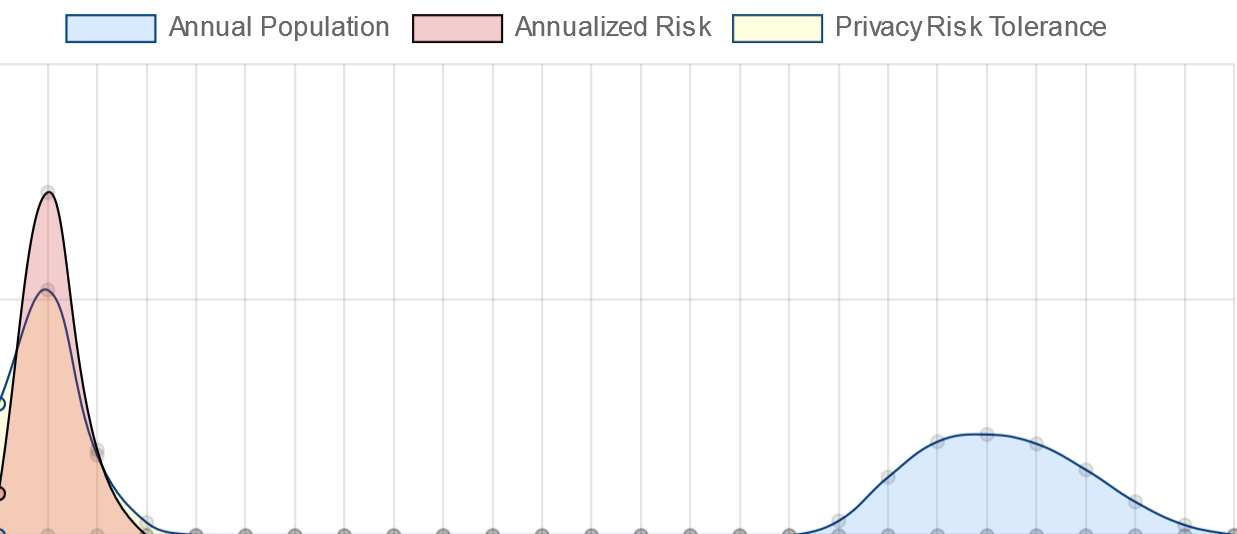 |
| Information Processing | |
 Aggregation Aggregation
combining of various pieces of personal information |
|
 Identification Identification
linking of information to a particular individual |
|
 Insecurity Insecurity
carelessness in protecting information from leaks or improper access |
|
 Secondary Use Secondary Use
using personal information for a purpose other than the purpose for which is was collected |
|
 Exclusion Exclusion
failing to let an individual know about the data that others have about them and participate in its handling or use |
|
| Information Dissemination | |
 Breach of Confidentiality Breach of Confidentiality
breaking a promise to keep a person's information confidential |
|
 Disclosure Disclosure
revealing truthful personal information about a person that impacts the ways others judge their character or impacts their security |
|
 Exposure Exposure
revealing an individual’s nudity, grief, or bodily functions |
|
 Increased Accessibility Increased Accessibility
amplifying the accessibility of personal information |
|
 Blackmail Blackmail
threatening to disclose personal information |
|
 Appropriation Appropriation
using an individual’s identity to serve the aims and interests of another |
|
 Distortion Distortion
disseminating false or misleading information about an individuals |
|
| Collection | |
 Surveillance Surveillance
watching, listening to, or recording of an individual's activities |
|
 Interrogation Interrogation
questioning or probing for personal information |
|
| Invasions | |
 Intrusion Intrusion
disturbing an individual’s tranquility or solitude |
|
 Decisional Interference Decisional Interference
intruding into an individual’s decision regarding their private affairs |
|